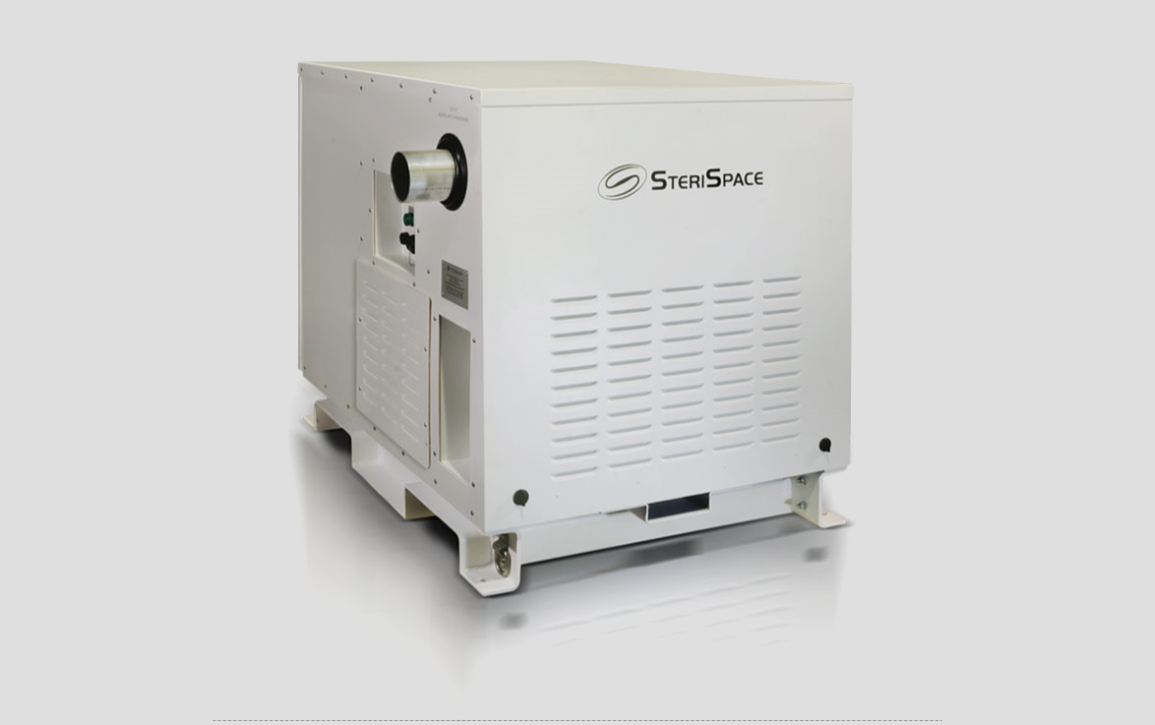
Measles case count hits 124 in ongoing West Texas outbreak
The number of confirmed measles cases reported in an outbreak in West Texas is now at 124, the Texas Department of Health Services said in an update Tuesday, an increase of 34 since late last week.

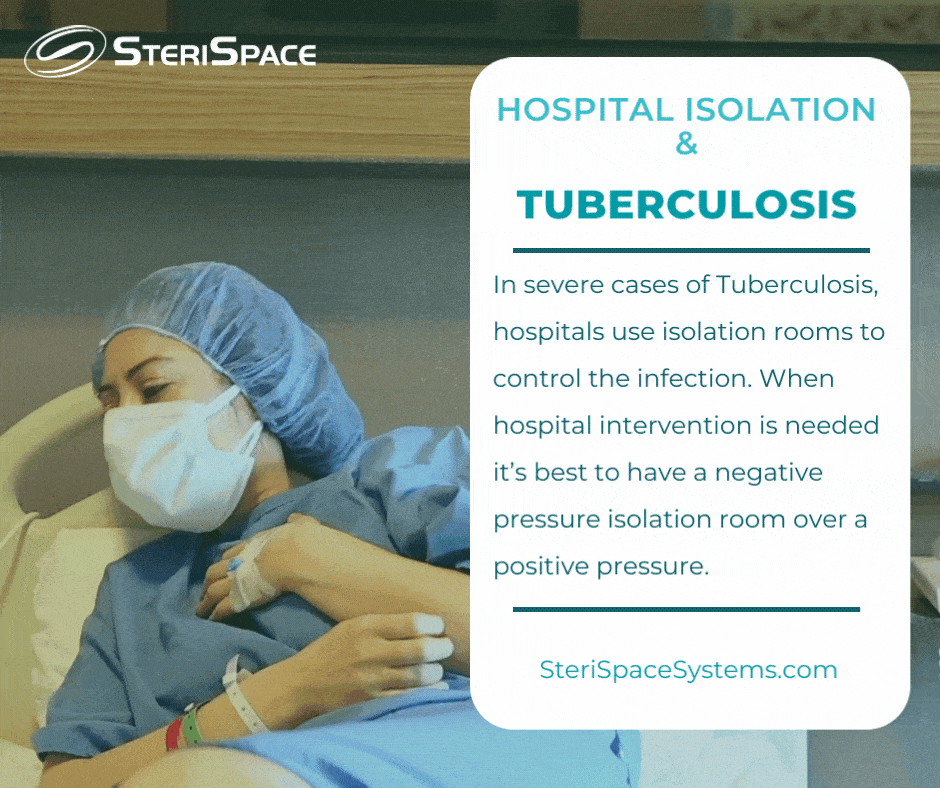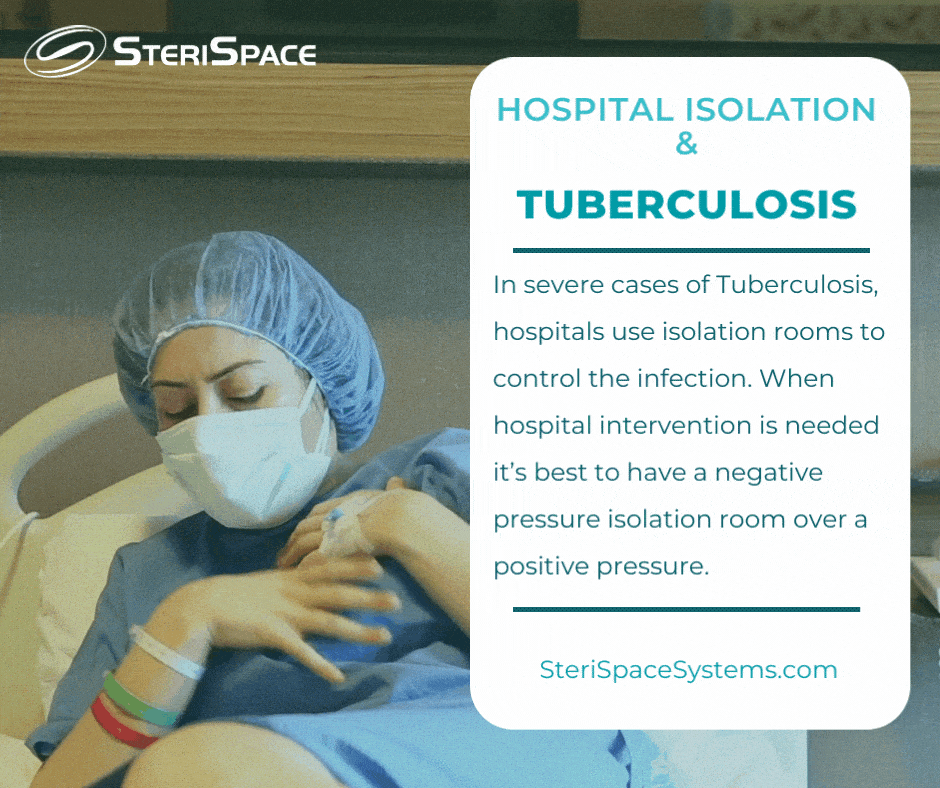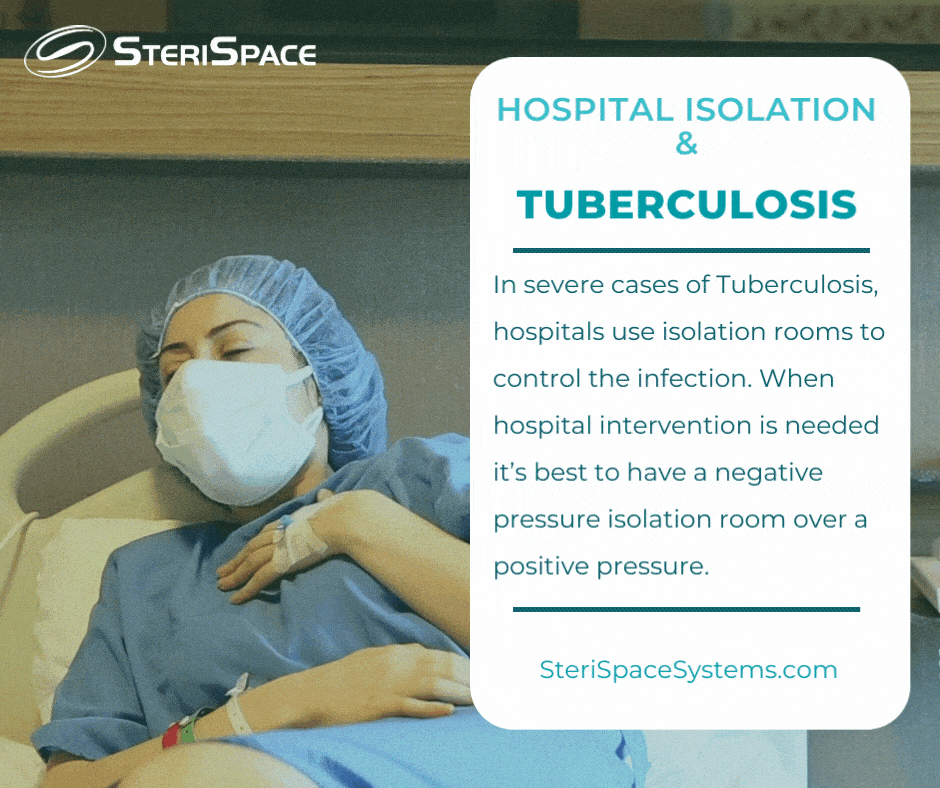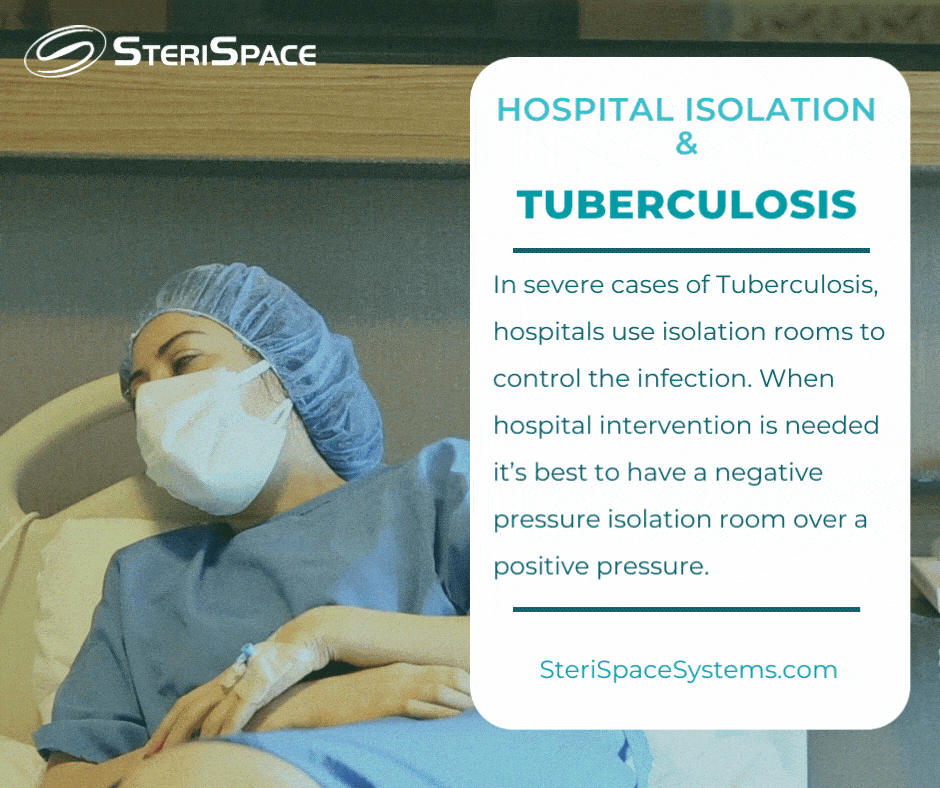 Airborne illnesses are the most contagious because the air all around you is contagious and in a continuous airflow. You don’t want anyone to breathe in the infected air. In severe cases,
Airborne illnesses are the most contagious because the air all around you is contagious and in a continuous airflow. You don’t want anyone to breathe in the infected air. In severe cases, 

